Resposta final para o problema
Solução explicada passo a passo
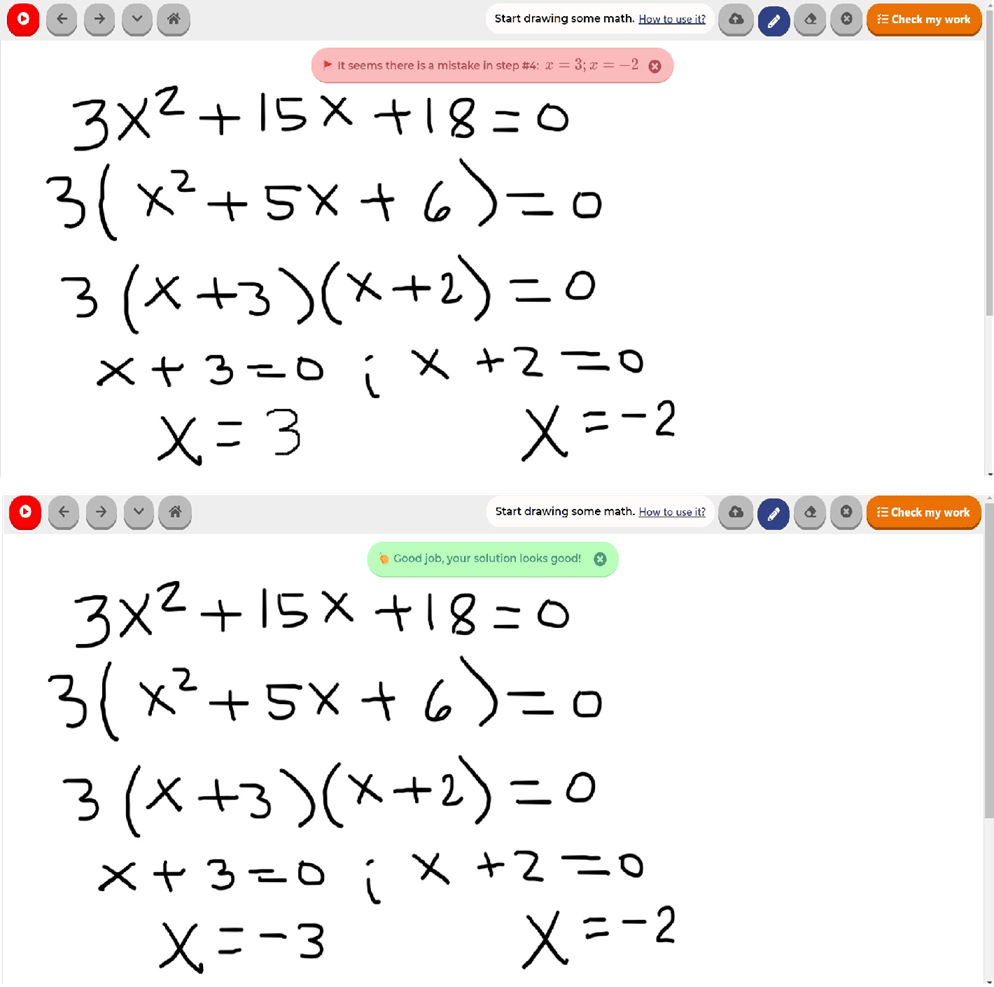
Como devo resolver esse problema?
- Escolha uma opção
- Derive usando a definição
- Encontre a derivada com a regra do produto
- Encontrando a derivada com a regra do quociente
- Calcule a derivada usando diferenciação logarítmica
- Encontre a derivada
- Integrar por frações parciais
- Produto de Binômios com Termo Comum
- Método FOIL
- Integrar por mudança de variável
- Carregue mais...
Aplicamos a regra: $\frac{d}{dx}\left(\ln\left(x\right)\right)$$=\frac{1}{x}\frac{d}{dx}\left(x\right)$
Aprenda online a resolver problemas derivada da soma passo a passo. d/dx(ln((1+cosh(x))/(1-cosh(x)))). Aplicamos a regra: \frac{d}{dx}\left(\ln\left(x\right)\right)=\frac{1}{x}\frac{d}{dx}\left(x\right). Aplicamos a regra: \frac{a}{\frac{b}{c}}=\frac{ac}{b}, onde a=1, b=1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right), c=1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right), a/b/c=\frac{1}{\frac{1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)}{1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)}} e b/c=\frac{1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)}{1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)}. Aplicamos a regra: \frac{d}{dx}\left(\frac{a}{b}\right)=\frac{\frac{d}{dx}\left(a\right)b-a\frac{d}{dx}\left(b\right)}{b^2}, onde a=1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right) e b=1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right). Aplicamos a regra: \frac{a}{b}\frac{c}{f}=\frac{ac}{bf}, onde a=1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right), b=1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right), c=\frac{d}{dx}\left(1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)\left(1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)-\left(1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)\frac{d}{dx}\left(1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right), a/b=\frac{1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)}{1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)}, f=\left(1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)^2, c/f=\frac{\frac{d}{dx}\left(1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)\left(1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)-\left(1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)\frac{d}{dx}\left(1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)}{\left(1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)^2} e a/bc/f=\frac{1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)}{1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)}\frac{\frac{d}{dx}\left(1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)\left(1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)-\left(1+\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)\frac{d}{dx}\left(1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)}{\left(1-\mathrm{cosh}\left(x\right)\right)^2}.