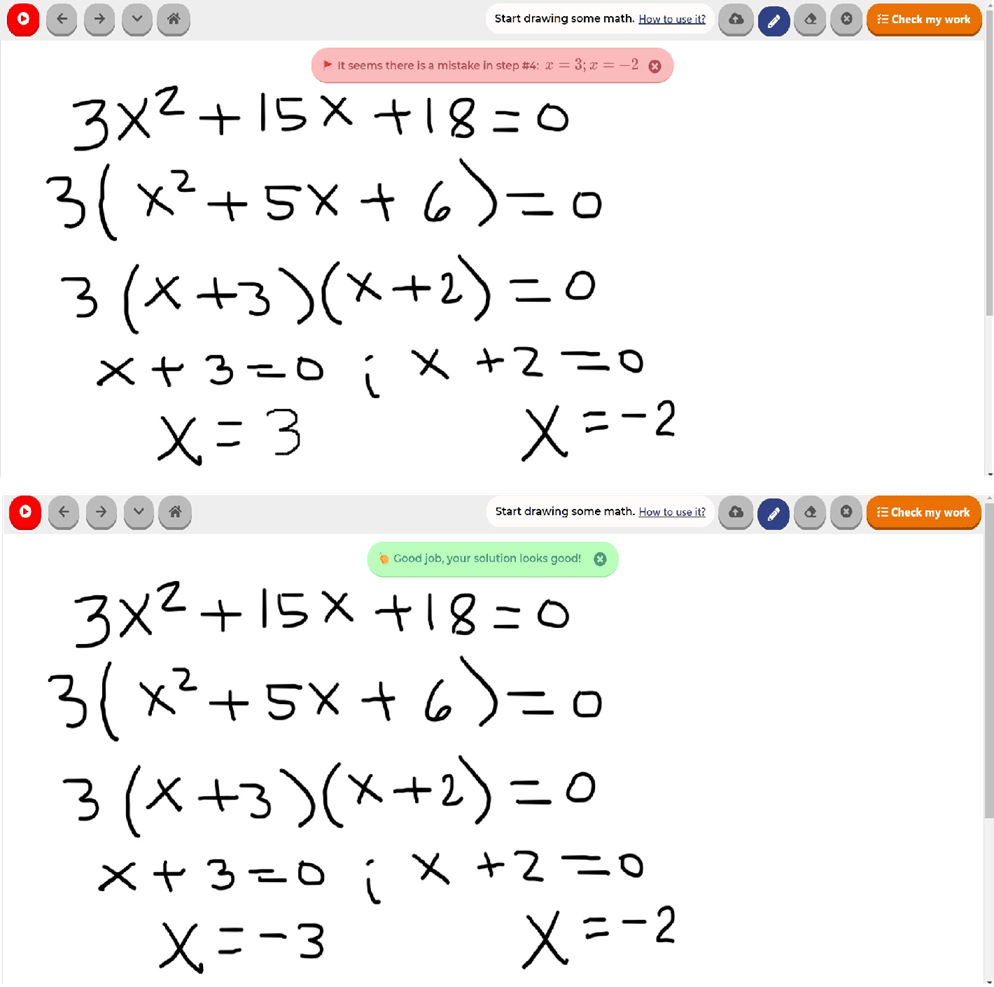
Resposta final para o problema
Solução explicada passo a passo
Como devo resolver esse problema?
- Escolha uma opção
- Integrar por frações parciais
- Integrar por mudança de variável
- Integrar por partes
- Integrar pelo método tabular
- Integrar por substituição trigonométrica
- Integração por Substituição de Weierstrass
- Integrar com identidades trigonométricas
- Integrar usando integrais básicas
- Produto de Binômios com Termo Comum
- Carregue mais...
Aplicamos a regra: $\int\frac{n}{x+b}dx$$=nsign\left(x\right)\ln\left(x+b\right)+C$, onde $b=-1$ e $n=1$
Aprenda online a resolver problemas passo a passo.
$\ln\left|x-1\right|$
Aprenda online a resolver problemas passo a passo. int(1/(x-1))dx&2&infinito. Aplicamos a regra: \int\frac{n}{x+b}dx=nsign\left(x\right)\ln\left(x+b\right)+C, onde b=-1 e n=1. Colocamos os limites iniciais de integração. Aplicamos a regra: \left[x\right]_{a}^{b}=\lim_{c\to b}\left(\left[x\right]_{a}^{c}\right)+C, onde a=2, b=\infty e x=\ln\left(x-1\right). Aplicamos a regra: \left[x\right]_{a}^{b}=eval\left(x,b\right)-eval\left(x,a\right)+C, onde a=2, b=c e x=\ln\left(x-1\right).